Have you ever thought about how you might talk to your little smart gadgets, like those that watch your home or help out with farming, even when they are far away? It's pretty neat, you know, to be able to check in on them, fix things, or give them new instructions without having to be right there. This idea of reaching out to devices that are not close by is becoming more and more common, especially with all the small computers and sensors popping up everywhere. It means you can keep an eye on things and make changes from your comfy chair, no matter where your device happens to be sitting.
These tiny bits of tech, often called Internet of Things or IoT devices, are doing all sorts of useful jobs, from keeping an eye on temperatures in big buildings to helping with how water flows in fields. But what happens if one of them starts acting a bit strange, or you need to send it a quick update? You can't always just go over to it and plug in a keyboard, can you? This is where having a way to connect to them from a distance really comes in handy. It's like having a secret pathway straight to your little machine, letting you send messages back and forth, which is pretty cool, actually.
And when we talk about doing this from a distance, a lot of people think about using big computer services that live on the internet, like Amazon Web Services, or AWS for short. AWS has a bunch of tools that can help you set up these connections, making sure they are safe and reliable. So, if you're wondering how you can get a direct line to your IoT gadget, even if it's in a different city or country, then getting to know how to use something called SSH with AWS is definitely something to think about. It's a very practical way to manage your scattered devices, you know, without much fuss.
Table of Contents
- What's the point of connecting to IoT devices from afar?
- How does remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example help?
- What exactly is SSH and why use it for IoT gadgets?
- Keeping things safe when you remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example.
- What parts of AWS help with remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example?
- Getting ready to remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example.
- How do you actually connect to your IoT device remotely using AWS?
- Looking after your remote connections for IoT devices.
What's the point of connecting to IoT devices from afar?
So, imagine you have a tiny little computer, maybe it's checking the temperature in your greenhouse, or keeping an eye on a water pump out in the fields, or perhaps it's just a smart light bulb in your living room. These are what we often call IoT devices, you know, Internet of Things gadgets. Now, what if something goes a little bit wrong with that temperature sensor? Or maybe you want to give the water pump some new instructions? You can't always just walk up to it and plug in a keyboard and screen, can you? Especially if it's far away, or, you know, stuck up high somewhere. That's where connecting to it from a distance comes in handy. It's really about being able to reach out and touch your devices, even when they're not right next to you, which is pretty useful, actually.
Being able to reach these devices remotely means you can keep them running smoothly without having to travel. Think about a whole bunch of sensors spread out across a big area. If one of them stops sending information, or if you need to update the little bit of computer code it's running, you want to be able to do that from your desk. It saves a lot of time and effort, and, you know, it can save money too. You might want to get some information off the device, like how much water has flowed through that pump today. Or maybe you just need to restart it because it's acting a bit funny. All these things become a lot simpler when you can talk to your device from wherever you are, which is, basically, the big idea here.
And it's not just about fixing problems, either. Sometimes, you just want to check in. Is that light bulb still connected to the network? Is the greenhouse sensor sending good numbers? You can use a remote connection to just peek in and see what's happening. It's like having a little window into what your devices are doing, no matter where they are. This kind of access, you know, it gives you a lot more control and peace of mind, especially when you have many devices doing important jobs. So, it's very much about staying connected and in charge of your gadgets, even when they're out of sight.
How does remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example help?
When you think about connecting to a device that's not in the same room, you need a way to do it safely. You don't want just anyone to be able to talk to your water pump or your smart light, right? That's where something like SSH comes into play. It's a way to make a very private and secure conversation line between your computer and the device. And when you add AWS into the mix, you get a whole set of tools that help manage these connections, making sure they are not only safe but also easy to set up and keep an eye on. It's like having a special, guarded path for your messages, which is pretty reassuring.
AWS offers different ways to help with this. For instance, it can help your little IoT device talk to the internet in a safe way, or it can give you a sort of middle-man computer that you connect to first, and then that middle-man connects to your device. This makes it so your IoT device doesn't have to be directly open to the whole internet, which is a good thing for safety, you know. It's kind of like having a special gatekeeper. This setup allows you to send commands, get information, and even update the software on your device, all from a distance, and all with a good level of protection. So, it's about making remote access simple yet very secure, actually.
So, if you have a bunch of devices scattered around, maybe in different buildings or even different parts of the world, using AWS to help with your remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example setup means you have a central place to manage everything. You can set up who can talk to which device, and make sure that only authorized people are making changes. This helps keep your whole system running smoothly and safely, which is, honestly, a big deal when you're dealing with lots of little machines doing important work. It gives you a lot of peace of mind, you know, knowing that your remote connections are handled well.
What exactly is SSH and why use it for IoT gadgets?
SSH stands for "Secure Shell." Think of it like a very special, locked tunnel for sending messages between two computers. When you use SSH, any information you send, like commands or files, gets scrambled up in a way that makes it very hard for anyone else to understand, even if they somehow manage to listen in. Then, when it reaches the other side, it gets unscrambled. This scrambling and unscrambling, you know, is what makes it "secure." It's a really old and trusted way for people to talk to computers from a distance, and it's used all over the place because it works so well at keeping things private.
For little IoT gadgets, SSH is super useful because these devices often don't have a screen or a keyboard attached to them. They're just sitting there, doing their job, maybe collecting data or turning things on and off. If you need to check their settings, see what they're doing, or even fix a small problem, you need a way to "log in" to them. SSH gives you that ability. It lets you open up a command window on your computer that's actually connected to the IoT device, so you can type commands as if you were sitting right in front of it. This is, basically, how you get direct control over your distant little machines.
The main reason to pick SSH for your IoT devices, especially when you're thinking about remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example, is its safety features. These small devices can be pretty vulnerable if they're just left open to the internet. SSH makes sure that only people with the right "keys" can get in. It's like having a very specific lock and key system. This means you can be pretty confident that only you, or someone you've given permission to, can access and control your devices. It's a reliable method for managing your small, scattered computers, which is, honestly, very important for security.
Keeping things safe when you remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example.
Keeping your remote connections safe is, you know, one of the most important things. When you're using SSH to talk to your IoT devices, especially through a service like AWS, there are a few simple steps you can take to make sure no one unwanted gets in. First off, you should always use something called "key pairs" instead of just passwords. A key pair is like having a super long, secret code that only you and the device know, and it's much harder for someone to guess than a typical password. You keep one part of the key on your computer, and the other part lives on the IoT device. This makes the connection very private, which is, actually, a good thing.
Another way to keep things safe when you remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example is to limit who can even try to connect. In AWS, you can set up what are called "security groups" or "network access control lists." These are like bouncers at a club, deciding who gets to come in. You can tell them, "Only allow connections from my office computer's internet address," or "Only allow connections from specific, known places." This helps stop random attempts to get into your devices, making it much harder for bad actors to even knock on the door. It's a very practical step to add an extra layer of protection.
Also, it's a good idea to keep the software on your IoT devices up to date. Just like you update the apps on your phone or the programs on your home computer, the little bits of code running on your IoT gadgets can have security fixes. Making sure these updates happen regularly helps close any little holes that might appear over time, which, you know, could otherwise be used by someone trying to get in. And finally, always make sure that the device itself is only running what it needs to run. The fewer extra programs or services it has, the fewer chances there are for someone to find a way in. These simple steps, basically, add up to a much safer remote setup.
What parts of AWS help with remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example?
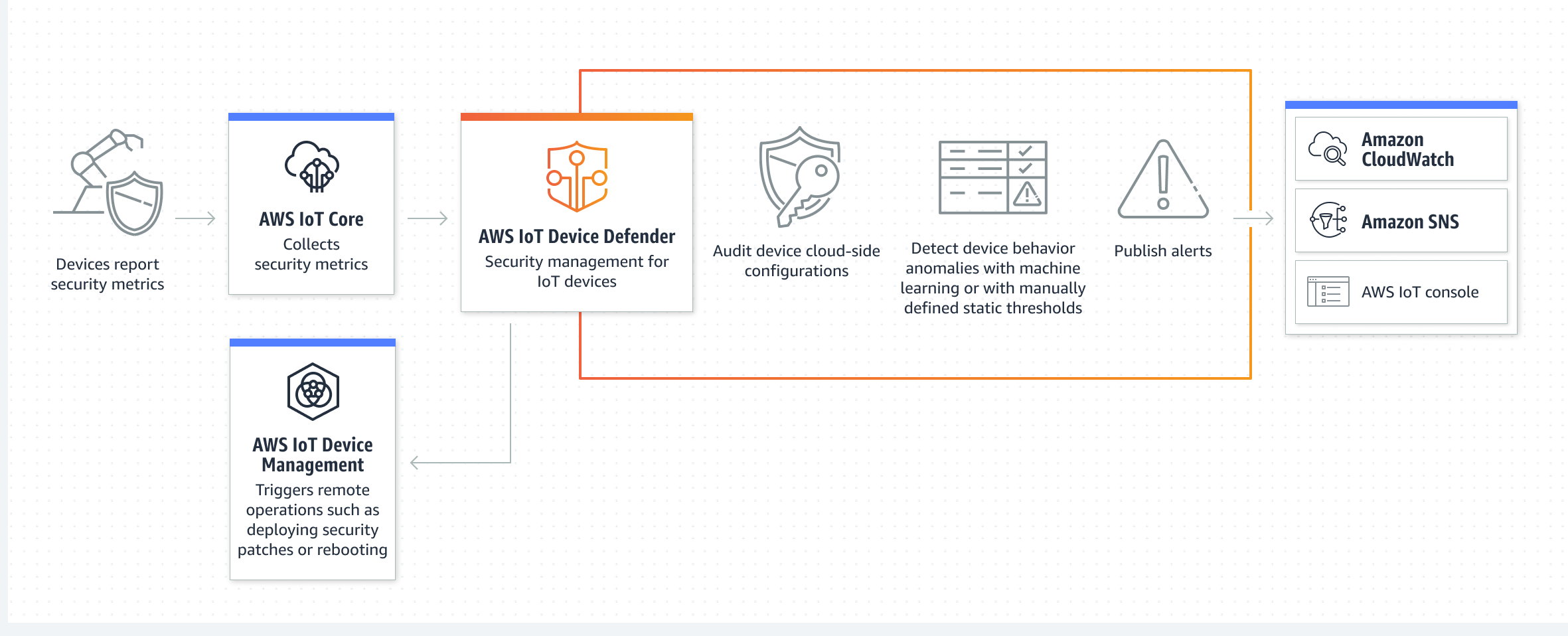
AWS has a whole bunch of services that can help you when you want to remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example. One of the main ones is AWS IoT Core. This service is like a big central hub where all your little IoT devices can connect and send their information. It helps manage the identities of your devices and makes sure they can talk to other AWS services safely. So, it's kind of the starting point for getting your devices online and ready to be managed from afar. It handles a lot of the tricky bits of getting devices connected to the internet, which is, you know, super helpful.
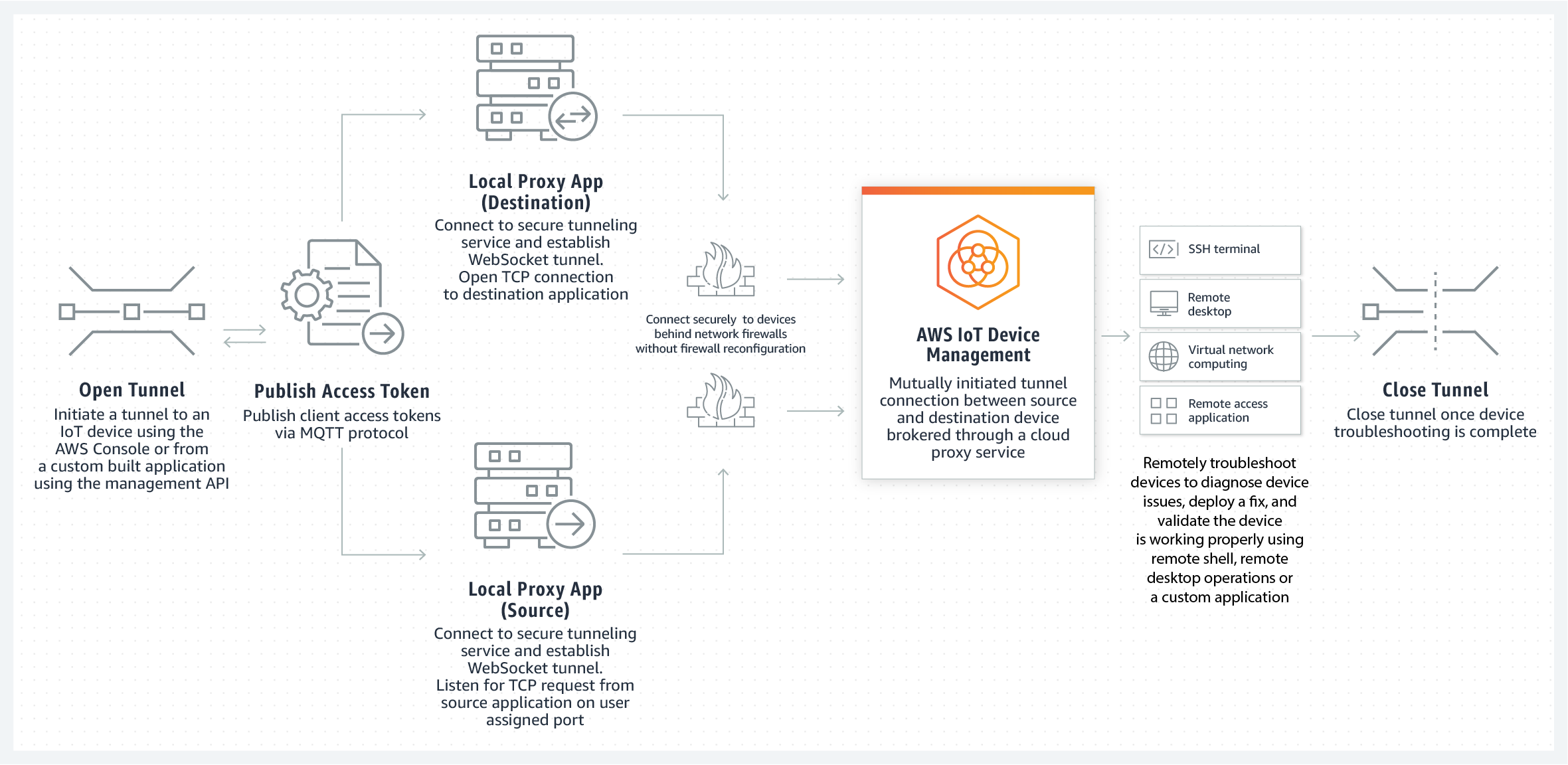
Then there's something called AWS Greengrass. This service lets you run some of your AWS services directly on your IoT devices themselves, even when they're not connected to the internet all the time. For remote access, Greengrass can help set up secure tunnels or ways for you to get to your device without it being directly exposed to the wide-open internet. It acts like a secure local agent that can receive commands and pass them along to the device, or even help start an SSH session. This adds another layer of control and safety for your remote connections, which is, frankly, a pretty clever way to do things.
You might also use something like an EC2 instance, which is basically a virtual computer you can run in AWS. People often set up a special EC2 instance called a "bastion host" or "jump box." This is a computer that you connect to first using SSH, and then from that computer, you SSH into your IoT device. It acts as a single, well-protected entry point. This means your IoT devices don't need to be directly reachable from your home or office internet connection, which, you know, makes them much safer. It's a very common way to manage remote access to many different kinds of devices, and it works well for IoT gadgets too.
Finally, AWS networking services, like Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and Security Groups, play a big part. A VPC is like your own private section of the internet inside AWS, where you can put your devices and other AWS resources. Security Groups, as we talked about earlier, act like firewalls, controlling what kind of traffic can go in and out of your devices or your bastion host. By using these networking tools, you can build a very controlled and safe path for your remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example connections, making sure only the right people and the right kinds of messages can get through. It's all about building a safe environment for your gadgets, you know, from the ground up.
Getting ready to remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example.
Before you can actually connect to your IoT device using SSH through AWS, there are a few things you need to get in order. First, your IoT device itself needs to be set up to accept SSH connections. This usually means it has a little bit of software running on it that listens for SSH attempts. You also need to make sure it has the right "key" installed, the public part of that key pair we talked about earlier. This key is what the device uses to make sure you are who you say you are when you try to connect, which is, essentially, the first step in making a secure link.
Next, you'll need to have an AWS account, of course, and set up some of the basic services. You'll likely need to get your IoT device registered with AWS IoT Core, so AWS knows it exists and can manage it. This often involves giving your device an identity and some permissions so it can talk to AWS. You might also need to set up that EC2 bastion host if you're going to use one, and make sure its security groups are configured to allow SSH connections from your computer. It's a bit like setting up all the pieces of a puzzle before you can put it together, you know.
You'll also need to have an SSH client on your own computer. This is just a program that lets you make SSH connections. Most computers that run Linux or macOS already have one built-in, and for Windows, you can use a program like PuTTY or the built-in OpenSSH client. You'll also need the private part of your SSH key pair on your computer. This is the secret half of the key that proves you're allowed to connect. So, getting your local computer ready with the right tools and keys is a pretty important step before you try to connect to your distant gadget, which is, honestly, quite straightforward once you know what you need.
How do you actually connect to your IoT device remotely using AWS?
Once everything is set up, actually making the connection to your IoT device from afar using AWS involves a few steps, but it's not as hard as it might sound. The most common way, as we mentioned, is to first connect to a "jump box" or bastion host that you've set up in AWS. So, from your own computer, you would open your SSH client and tell it to connect to the public address of your bastion host, using your private SSH key for safety. This is the first secure hop in your journey to the IoT device, you know, like getting on the first train of a two-part trip.
After you're successfully connected to your bastion host, you're now inside the AWS network, in a way. From there, you can then make a second SSH connection, this time from the bastion host to your actual IoT device. Your IoT device might have a private address within your AWS private network, which makes it even safer because it's not directly exposed to the internet. You'd use the command line on your bastion host to initiate this second SSH connection, again using the appropriate private key for the IoT device. It's a bit like taking a second, internal train to your final destination, which is, basically, how you get to your device securely.
Some AWS services, like AWS IoT Device Shadow or AWS IoT Greengrass, can also help facilitate this. For example, Greengrass can create a secure tunnel directly to your device, or allow you to run commands on the device without needing a direct SSH session in the traditional sense. These methods often involve the IoT device checking in with AWS IoT Core, and then AWS can send commands or set up a temporary connection for you. So, there are different paths you can take, but the core idea is always about creating a safe, authenticated way to send instructions and get information from your distant gadget. It's really about picking the method that fits your specific needs, actually.
The exact commands you type will depend on your specific setup, but the general idea is always the same: authenticate yourself with keys, and then tell your SSH client where to connect. If you're using a bastion host, you'll have two separate SSH commands, one after the other. If you're using a more direct method through AWS IoT services, the process might be a bit more automated on the AWS side, but the underlying safety principles are still there. It's all about making sure that every step of the connection is verified and private, which is, honestly, what makes remotely SSH to IoT device AWS example so reliable for managing your gadgets from a distance.